Living with Arthritis? Discover How to Take Control of Your Symptoms
Arthritis is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling in the joints. It can impact people of all ages, although it is more common in older adults. Living with arthritis can be challenging, but there are ways to take control of your symptoms and improve your quality of life. Whether you have osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or any other form of the disease, this article will explore practical steps you can take to manage your symptoms effectively.
How to Take Control of Your Arthritis Symptoms
While arthritis cannot be completely cured, there are several ways to manage and reduce its symptoms. With the right approach, it is possible to maintain an active and fulfilling lifestyle. Here are some strategies to help you take control of your arthritis:
1. Stay Active: Exercise Is Key
It may seem counterintuitive to exercise when your joints are painful, but staying active is one of the best ways to manage arthritis symptoms. Regular physical activity helps to:
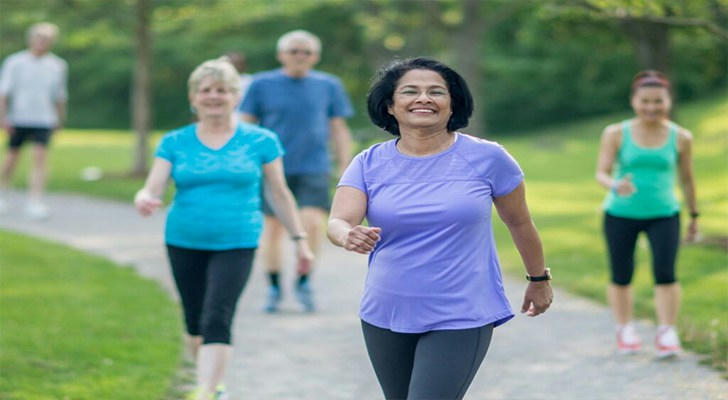

•Improve joint flexibility and range of motion: Gentle exercises such as stretching, yoga, and swimming can improve the flexibility of your joints, reducing stiffness and helping you move more easily.
•Strengthen muscles: Strong muscles support and protect your joints, reducing the strain on them.
•Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight puts added pressure on your joints, especially the knees, hips, and lower back. Regular exercise helps with weight management, which can reduce pain.
Low-impact exercises are ideal for people with arthritis. Some great options include:
•Swimming or water aerobics: The buoyancy of water helps reduce pressure on the joints while still providing a good workout.
•Walking: Walking is a simple and accessible way to stay active.
•Yoga and Pilates: These practices help improve flexibility, balance, and strength.
•Cycling: Riding a stationary bike or cycling outdoors is another low-impact exercise that can improve joint function.
Before starting any new exercise program, it’s important to consult with your doctor or physical therapist to ensure the exercises are suitable for your condition.
2. Manage Pain with Medication
While there is no cure for arthritis, there are many medications available that can help alleviate pain and inflammation. Depending on the type and severity of your arthritis, your doctor may recommend:
•Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen and naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
•Acetaminophen: This pain reliever is effective for managing mild to moderate arthritis pain.
•Topical creams and gels: These can be applied directly to the affected joint for localized pain relief.
•Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): These are often prescribed for rheumatoid arthritis to slow the progression of the disease and reduce inflammation.
•Corticosteroids: These medications can be taken orally or injected directly into the joint to reduce severe inflammation.
It’s important to follow your doctor’s recommendations when using medications, as they may have side effects, especially if used long-term.
3. Use Hot and Cold Therapy
Hot and cold treatments can be simple and effective ways to manage arthritis symptoms. Heat can help relax muscles and improve blood flow, while cold can numb pain and reduce swelling. Here’s how to use them:
•Hot packs: A warm bath, heating pad, or warm towel can help ease stiffness and relax muscles. Use heat for about 15-20 minutes at a time.
•Cold packs: Ice or cold packs can help reduce swelling and numb pain in inflamed joints. Apply cold therapy for 10-15 minutes, making sure to have a layer between the ice and your skin to prevent frostbite.
Switching between hot and cold therapies can be particularly effective if your arthritis symptoms include both swelling and stiffness.
4. Eat a Healthy Diet
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in managing arthritis. Certain foods have anti-inflammatory properties, while others can exacerbate inflammation. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce symptoms:
•Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, omega-3s can help reduce inflammation. If you're vegetarian or vegan, consider flaxseeds or chia seeds as an alternative.
•Fruits and vegetables: These are packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that promote joint health. Leafy greens, berries, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower are particularly beneficial.
•Whole grains: Brown rice, oats, and quinoa provide fiber and nutrients that can help reduce inflammation.
•Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and sunflower seeds are rich in healthy fats and can support joint health.
On the other hand, it’s important to limit processed foods, sugar, and excessive alcohol consumption, as they can trigger or worsen inflammation.
5. Consider Supplements
Several supplements are believed to help manage arthritis symptoms, although it’s important to talk to your doctor before adding them to your routine. Some commonly used supplements for arthritis include:
•Glucosamine and chondroitin: These compounds are thought to help maintain cartilage and reduce joint pain, especially in osteoarthritis.
•Turmeric/curcumin: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, turmeric has been shown to provide relief from arthritis pain.
•Fish oil: The omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil may help reduce joint stiffness and pain.
While these supplements can provide relief, they should not replace conventional treatments unless approved by your healthcare provider.
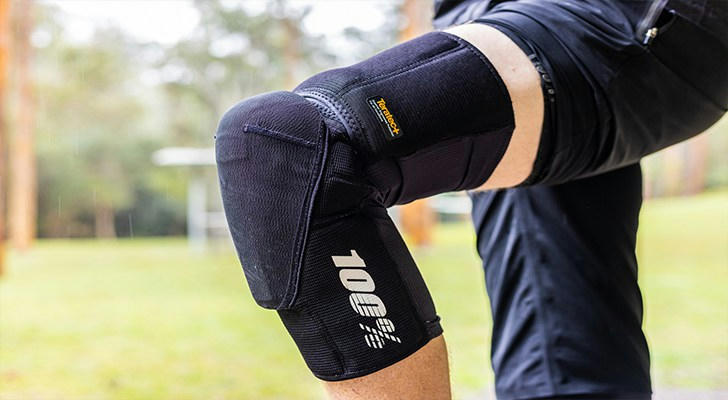
6. Supportive Devices and Joint Protection
Using assistive devices and practicing joint protection techniques can help reduce the strain on your joints during daily activities. Some helpful tools include:

•Orthotic shoes: Proper footwear can provide support and reduce pain in the knees, hips, and back.
•Splints and braces: These devices can help stabilize the joints and prevent excessive movement, reducing pain and preventing further damage.
•Ergonomic tools: Devices such as electric can openers, jar grips, and long-handled reachers can make daily tasks easier and reduce joint stress.
Additionally, practicing good posture and using proper body mechanics when lifting or performing activities can help protect your joints.
7. Mental Health Matters
Living with arthritis can be emotionally challenging. The constant pain and limitations can lead to feelings of frustration, stress, or even depression. It’s important to prioritize your mental well-being. Consider the following strategies:
•Mindfulness and meditation: These practices can help you manage stress and improve your emotional well-being.
•Support groups: Connecting with others who understand what you’re going through can provide emotional support and useful coping strategies.
•Counseling: Talking to a therapist can help you manage the mental health challenges that come with living with chronic pain.
While arthritis can significantly affect your daily life, there are many ways to take control of your symptoms and continue living an active and fulfilling life. By incorporating regular exercise, managing pain with medications, using hot and cold therapy, eating a healthy diet, and considering supplements, you can improve your joint health. Additionally, using supportive devices and protecting your joints can prevent further damage. Don’t forget to prioritize your mental health, as managing stress and connecting with others can help you live with arthritis more effectively. Always work with your healthcare team to create a personalized plan that works best for you, and take small, consistent steps toward improving your quality of life.
